|
Regular eye exams are an invaluable tool in maintaining healthy eyes by detecting and preventing disease. Some diseases develop slowly without causing pain or vision loss. Early detection of any problems can reduce the risk of further harm and allow for a choice of treatment options. The entire exam process can take an hour depending on the complexity of the problem. Each patient will be evaluated with a refraction, slit lamp, intraocular pressure and a retinal exam.
|
Comprehensive Vision and Eye Health Examinations |
|
Pediatric Eye Care
We take pride in maintaining the vision of our younger patients in an environment that is lighthearted and fun. We want to insure the good sight, vision, and eye health for the rest of your child's life and take a preventative approach to his/her general health and eye health. We will work with your child's primary care physician to help keep his/her eyes healthy. It is important that all of our pediatric patients have healthy and efficient visual systems to help make visual demands of learning in school easier and fun. |
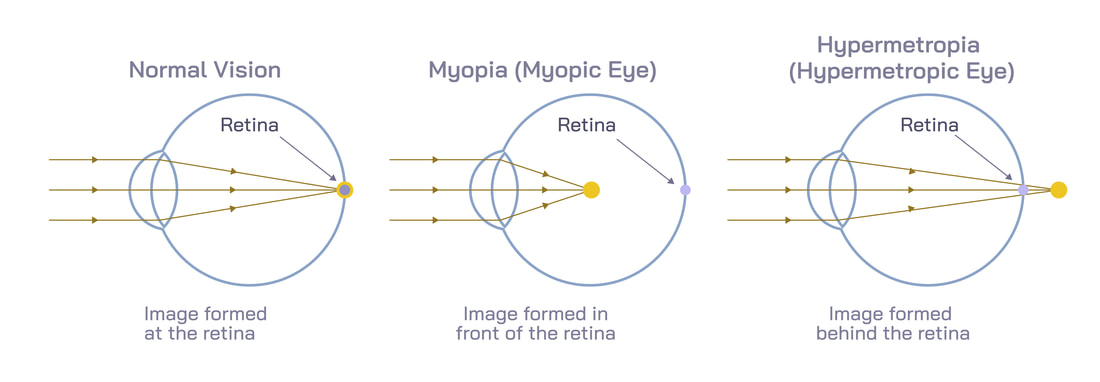
Vision Conditions
|
|
Myopia (Nearsightedness)
Nearsightedness, medically known as myopia, refers to vision that is good at close range but not at a distance. It generally occurs because the eyeball is too “long” as measured from front to back. Nearsightedness is diagnosed during routine eye exams and possible treatments include eyeglasses, contacts, acrylic corneal implants, LASIK, radial keratotomy (RK) and photorefractive keratotomy (PRK). |
Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
Farsightedness, medically known as hyperopia, refers to vision that is good at a distance but not at close range. Farsightedness occurs when the eyeball is shorter than normal, as measured from front to back, or when the cornea has too little curvature. This reduces the distance between the cornea and retina, causing light to converge behind the retina, rather than on it. If you are mildly farsighted, your eye care provider may not recommend corrective treatment at all. However, if you are moderately or severely hyperopic, you may have several treatment options available, including eyeglasses, contacts, LASIK and photorefractive keratectomy (PRK). |
|
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is an uneven or irregular curvature of the cornea or lens, which results in blurred or distorted vision. Other symptoms of astigmatism include the need to squint, eye strain from squinting, headaches and eye fatigue. In reality, most people have some degree of astigmatism, which is usually present at birth and is believed to be hereditary. In minor cases, treatment may not be required but is certainly beneficial. Moderate to severe astigmatism can be treated with corrective eyewear or LASIK surgery. |
|
Presbyopia (Aging Eyes)
If you're over 40 years old, you may find that your vision needs have begun to change. You may be having more trouble with reading fine print, requiring the use of reading glasses or other aids to make out what's on the menu at your favorite restaurant. Aging eyes, medically known as presbyopia, is a condition in which the lens of the eye gradually loses its flexibility, making it harder to focus clearly on close objects such as printed words. Distance vision, on the other hand, is usually not affected. Unfortunately, presbyopia is an inevitable part of aging and cannot be prevented by diet, lifestyle or visual habits. However, it is treatable with several types of corrective lenses, including progressives, bifocals and trifocals, single-vision reading glasses, multifocal contact lenses and monovision therapy. |